The Role of 3PL and 4PL Partnerships in an Evolving Logistics Ecosystem
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, supply chains are under constant pressure to become faster, more resilient, and more efficient. Companies are navigating global disruptions, shifting customer expectations, and new technologies that demand smarter logistics strategies.
At the center of this transformation are third-party logistics (3PL) and fourth-party logistics (4PL) providers—strategic partners that enable businesses to focus on core competencies while improving logistics performance. Understanding the differences between 3PL and 4PL services—and how they work together—can help companies choose the right level of logistics support to thrive in a competitive global market.
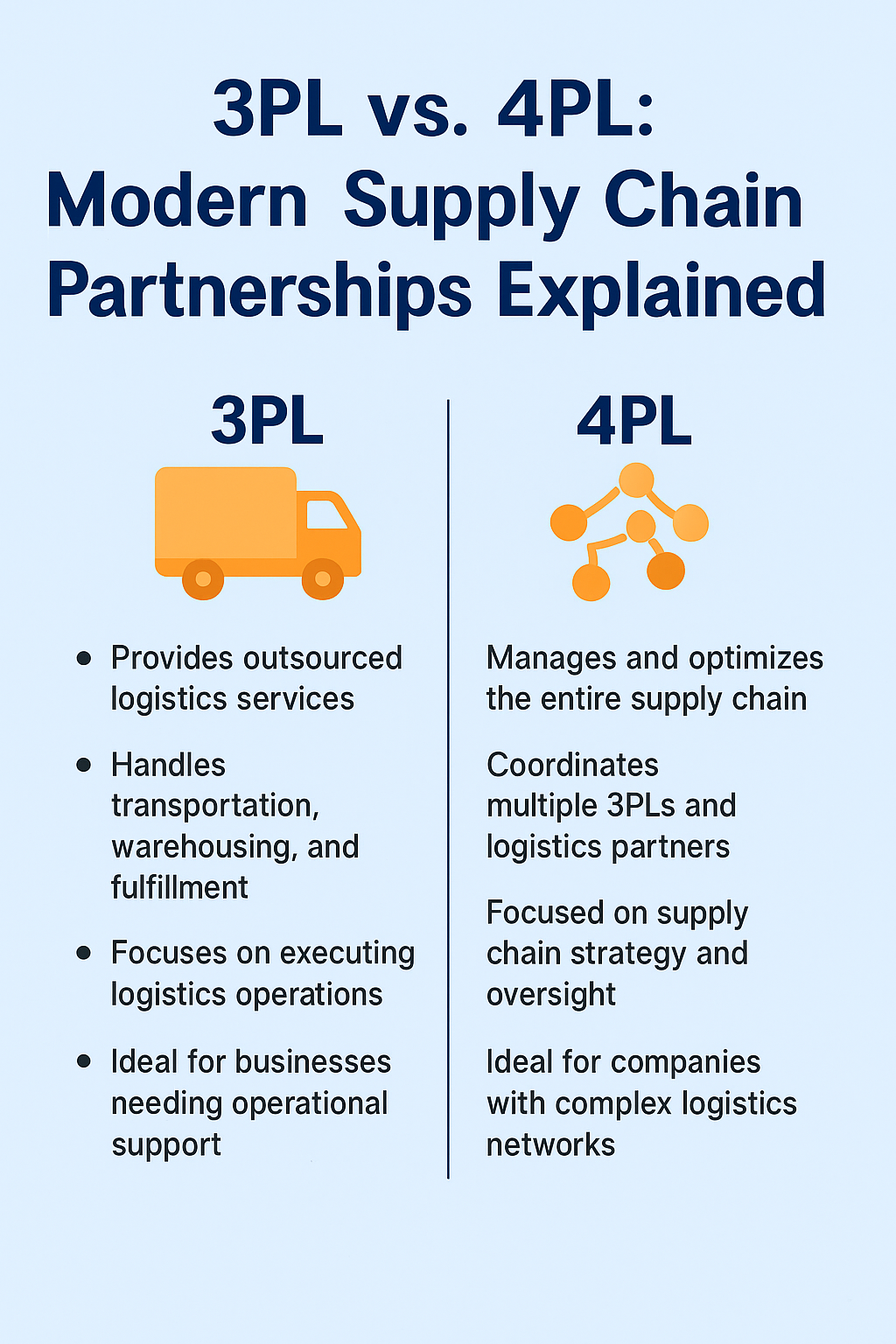
What Is a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics Provider)?
A 3PL provider offers outsourced logistics services, typically handling one or more parts of a company’s supply chain. These services often include transportation, warehousing, inventory management, fulfillment, and distribution.
Essentially, a 3PL acts as an operational extension of a business. By partnering with a 3PL, companies can leverage the provider’s infrastructure, expertise, and technology to streamline logistics without investing heavily in their own assets.
Common 3PL services include:
Freight transportation and carrier management
Warehousing and inventory control
Order fulfillment and distribution
Reverse logistics and returns management
Customs brokerage and cross-border support
For example, a retailer might partner with a 3PL to manage warehousing and delivery during peak holiday seasons. This allows them to scale up operations quickly without hiring additional staff or acquiring new storage space.
What Is a 4PL (Fourth-Party Logistics Provider)?
A 4PL provider, on the other hand, takes logistics outsourcing a step further. While a 3PL focuses on executing logistics operations, a 4PL oversees and optimizes the entire supply chain ecosystem—including multiple 3PLs and other logistics partners.
A 4PL serves as a strategic integrator, offering end-to-end supply chain management, visibility, and coordination. They typically do not own physical assets like trucks or warehouses. Instead, they manage logistics networks through data, technology, and partnerships.
Typical 4PL services include:
Supply chain design and optimization
Technology integration and data analytics
Multi-partner coordination and vendor management
Strategic planning and performance monitoring
Risk management and cost optimization
Where a 3PL executes, a 4PL orchestrates. This makes 4PLs ideal for complex, global supply chains that require centralized control and advanced visibility.
3PL vs. 4PL: Key Differences
While both 3PLs and 4PLs help businesses improve logistics performance, their roles and value propositions differ significantly.
In short, a 3PL helps you do logistics better, while a 4PL helps you rethink and manage logistics strategically.
The Shifting Logistics Landscape: Why These Partnerships Matter
Global supply chains are becoming more complex due to factors like e-commerce growth, nearshoring, sustainability demands, and digital transformation. These shifts are driving companies to look for more flexible, intelligent logistics partnerships.
Here are a few key trends shaping 3PL and 4PL partnerships today:
1. Digital Transformation and Data Visibility
Modern supply chains rely heavily on data-driven decision-making. 3PLs and 4PLs are investing in advanced transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse management systems (WMS), and AI-driven analytics to provide real-time visibility and predictive insights.
A 4PL, in particular, uses these technologies to integrate data from multiple logistics providers and provide a unified view of performance metrics, inventory levels, and shipment tracking.
2. The Rise of E-Commerce and On-Demand Logistics
The e-commerce boom has redefined delivery expectations. Consumers now demand faster shipping, flexible delivery windows, and transparent tracking. 3PLs have responded by expanding fulfillment center networks and last-mile delivery capabilities. 4PLs complement this by coordinating multiple 3PLs to ensure seamless, omnichannel logistics operations.
3. Sustainability and Green Logistics
Sustainability has become a strategic priority for global supply chains. Both 3PLs and 4PLs are helping companies reduce emissions through smarter route planning, modal optimization, and green warehousing. A 4PL can integrate sustainability metrics across all logistics partners—helping companies track carbon footprints and implement greener strategies holistically.
4. Resilience and Risk Management
Supply chain disruptions—from pandemics to geopolitical events—have shown the need for resilience. 4PLs play a key role here by creating contingency plans, diversifying suppliers, and using predictive analytics to anticipate potential disruptions. 3PLs then execute these strategies at the operational level, ensuring agility when conditions change.
How 3PL and 4PL Partnerships Work Together
Rather than viewing 3PL and 4PL models as competitors, forward-thinking businesses are recognizing that they can complement each other.
A 4PL often manages multiple 3PLs within a unified supply chain strategy. For instance:
A 3PL may handle domestic transportation and warehousing.
Another 3PL might manage international freight forwarding.
The 4PL oversees both, ensuring smooth coordination, optimized costs, and data consistency across partners.
This layered approach allows companies to maintain operational excellence while gaining strategic oversight.
Benefits of Partnering with a 3PL or 4PL
Benefits of 3PL Partnerships
Reduced logistics costs through economies of scale
Access to specialized expertise and technology
Improved delivery performance and customer satisfaction
Flexibility to scale operations up or down seasonally
Benefits of 4PL Partnerships
Centralized visibility across the entire supply chain
Strategic alignment with business goals
Streamlined vendor management and coordination
Data-driven optimization and continuous improvement
Ultimately, the choice between a 3PL and 4PL depends on a company’s supply chain complexity, size, and long-term strategy.
How to Choose the Right Partner
When evaluating logistics partners, consider the following key factors:
Your Supply Chain Complexity
If you primarily need warehousing or transportation help, a 3PL is often sufficient. For integrated supply chain oversight, a 4PL offers greater strategic value.
Technology Capabilities
Look for partners that leverage cloud-based platforms, real-time analytics, and integration capabilities with your internal systems.
Scalability and Flexibility
Your logistics provider should be able to adapt to growth, seasonal demand, and market shifts without compromising performance.
Cultural and Strategic Alignment
The best partnerships go beyond contracts—they’re built on trust, transparency, and shared goals.
The Future of 3PL and 4PL in the Logistics Ecosystem
The line between 3PL and 4PL services is becoming increasingly blurred as technology reshapes logistics. Many 3PLs are adopting advanced data platforms and strategic capabilities, while some 4PLs are expanding their operational roles.
Looking ahead, we can expect:
Greater integration between digital supply chain platforms and physical operations.
AI and automation driving predictive decision-making.
Sustainability metrics embedded into logistics KPIs.
Collaborative ecosystems where 3PLs, 4PLs, and shippers share data for continuous improvement.
The future of logistics will not be defined by a single provider type—but by the strength of partnerships and the ability to adapt together in an ever-changing market.